Connect to Azure SQL database using managed identity C# .Net 6.0
Let's discuss the connecting .net 6.0 c# application to azure SQL serve using MSI
.NET 6.0 applications are more flexible and require less work than other.NET frameworks, such as.NET Core 3.1,.NET 4.8, and so on.
Connect .Net Core 3.1 or the Lower version Application to azure SQL
you will be using the following package
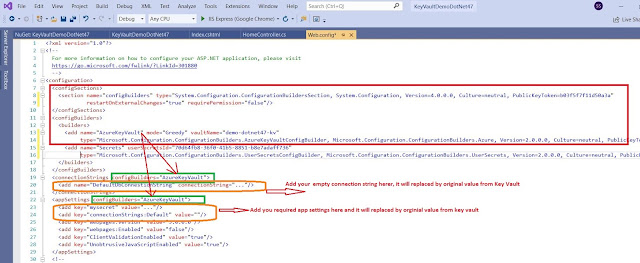
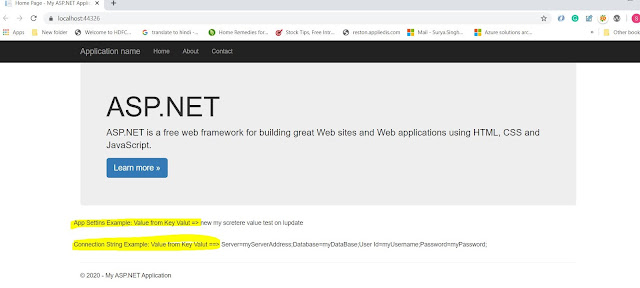
Connect .Net 6.0 Application to Azure SQL:
you will be using only following the NuGet package with the new connection string
if you are using system-assigned identity MSI then uses the following connections string and code.(Local Machine)
Set up your dev environment and Visual Studio
- Visual Studio for Windows is integrated with Azure AD authentication. To enable development and debugging in Visual Studio, add your Azure AD user in Visual Studio by selecting File > Account Settings from the menu, and selecting Sign-in or Add.
- To set the Azure AD user for Azure service authentication, select Tools > Options from the menu, then select Azure Service Authentication > Account Selection. Select the Azure AD user you added and select OK